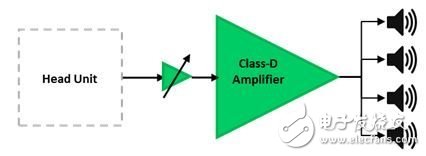
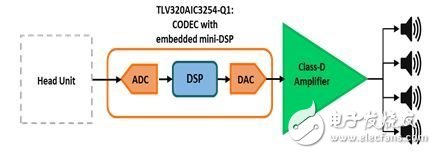
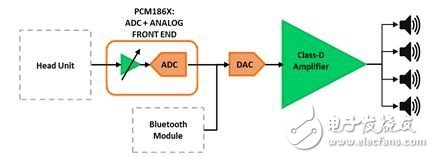
In order to improve the driving and passenger experience, the current vehicles, regardless of size, price, entertainment and information functions are provided more and more. Today's pre-installed infotainment systems typically combine entertainment, multimedia and driver information in one module. They offer AM/FM and satellite radio, a CD/DVD player for playing music and videos, a navigation system, data and multimedia ports (USB, Bluetooth®, line in, line out, video input), as well as general and vehicle status. information. Until recently, even the best factory pre-installed systems offered a lower-than-average level of listening experience for discerning users. When users demand excellent car audio quality, upgrading the factory pre-installed system with spare parts with greatly improved quality was once an inevitable choice. Today, in high-end vehicles, quality original equipment manufacturer (OEM) products can catch up with and even exceed the same after-sales system in almost every respect. In addition to the audio console infotainment system, these high-end systems include powerful, pre-installed external amplifiers that are separate from the audio host for better sound quality. For mid- to low-end vehicles with basic audio consoles and no external amplifiers, adding an external aftermarket amplifier greatly improves sound quality; see Figure 1. Figure 1: Low-end automotive amplifiers: discrete preamplifiers and amplifiers In a typical system, the power amplifier has three parts: a preamplifier, from which the signal enters the amplifier, and where devices such as dividers and equalizers are located; the power supply that powers the amplifier; and the amplifier itself that drives the speaker . It is possible for the preamplifier portion of the amplifier to have a gain control stage; it controls the amplification of the audio host signal to drive the amplifier to its maximum power level. Depending on the amplifier topology, this control stage can be implemented with discrete op amps and discrete components, as well as a fully integrated analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with an analog front end or CODEC solution. The preamplifier stage of the higher-end amplifier can also perform some level of signal processing to improve the audio output (such as frequency division or equalization); this signal processing occurs in the digital domain using a processor or digital signal processor (DSP) . The fully integrated audio codecs with embedded miniDSP converts the input audio analog signal into digital information, performs audio signal enhancement, and converts it back to an analog signal. The operational flow is shown in the system block diagram in Figure 2. Other alternative topologies include discrete ADC or digital-to-analog converter (DAC) combinations that increase system flexibility; see Figure 3. Figure 2: Mid-Range Automotive Amplifier: Integrated Preamplifier with Gain Control and EQ For the actual amplifier stage, by using Class D audio amplifiers, the system's power efficiency can exceed 90% while maintaining top-line audio fidelity. This efficiency has greatly reduced size, weight and heat dissipation; in addition, while Class D audio amplifiers require external inductors, new lower cost automotive grade inductors allow system designers to cut system costs and with smaller externalities Size achieves similar functionality to Class AB based audio systems. Figure 3: High Car Amplifier: Integrated Preamplifier with Analog Gain Control, Crossover, and EQ TI's Class D automotive audio amplifiers exhibit extremely low levels of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and are used with stringent electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) requirements without additional (and expensive) filtering or shielding (such as CISPR 25-L5) in the OEM system. Automotive systems are often subject to extreme working conditions and require an enhanced level of reliability in execution. TI's full capabilities include load diagnostics for detecting and diagnosing output disconnects to help reduce test time during manufacturing, as well as load dump protection against high voltage transients commonly found in automotive system power supplies. Other resources: Read this blog post to learn how to keep out-of-band noise low. Visit TI's. Learn more about TI's Class D amplifiers. Shenzhen Esun Herb Co.,Ltd. , https://www.szyoutai-tech.com